HSE Plan Sample
An HSE plan is a strategic document that provides guidance on health, safety, and environmental management for any project. In certain cases, formulas are needed to assess risks, calculate safety metrics, or measure environmental impact. Here’s an updated sample that includes relevant formulas for risk assessment and safety performance.
HSE Plan Sample
Explore a detailed HSE plan sample that outlines essential components for workplace safety, risk management, and environmental protection. Ensure compliance and promote a culture of safety with this practical guide.
Project Name: ABC Construction Project
Company Name: XYZ Construction Pvt. Ltd.
Project Location: [Location]
Date: [Insert Date]
1. Introduction
This Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Plan defines the procedures and responsibilities for ensuring the safety, health, and environmental protection of all personnel involved in the ABC Construction Project. The plan outlines the strategies for hazard identification, risk management, emergency preparedness, and environmental sustainability.
2. Objectives
The key objectives of this HSE Plan are:
- To prevent workplace injuries and incidents.
- To comply with all relevant HSE laws, regulations, and standards.
- To promote a culture of safety and environmental responsibility.
- To minimize environmental impacts related to construction activities.

3. Responsibilities
Project Manager
- Oversee the implementation of the HSE Plan.
- Ensure resources are allocated for HSE compliance.
- Monitor the effectiveness of the HSE Plan.
- Conduct regular safety audits and inspections.
- Train employees and subcontractors on HSE procedures.
- Report safety incidents and maintain records.
Supervisors
- Enforce safety procedures on-site.
- Ensure that workers use personal protective equipment (PPE).
Employees
- Adhere to all safety protocols.
- Report unsafe conditions and incidents immediately.
4. Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification
A thorough risk assessment has been conducted for the ABC Construction Project. Here are some potential hazards identified:
- Working at Heights: There is a risk of falling while working on elevated platforms.
- Heavy Machinery: Operating construction equipment, such as cranes and excavators, can pose hazards.
- Electrical Hazards: Workers may be exposed to live wires and electrical circuits.
- Slip, Trip, and Fall Hazards: Uneven surfaces and debris at the site increase the risk of falls.
How to Assess Risk
To determine the risk level for each hazard, we use a simple formula:
Risk=Likelihood of Occurrence×Severity of Consequences
Likelihood: This is rated on a scale from 1 to 5, where:
- 1 = Rare
- 2 = Unlikely
- 3 = Possible
- 4 = Likely
- 5 = Almost Certain
Severity: This is also rated on a scale from 1 to 5, where:
- 1 = Minor Injury
- 2 = Moderate Injury
- 3 = Serious Injury
- 4 = Major Injury
- 5 = Fatal or Severe Injury
Example Calculation
Let’s say we assess the risk of falling from height:
- Likelihood: 3 (Possible)
- Severity: 4 (Serious Injury)
Using the formula, the risk score would be:
Risk=3×4=12
This score indicates a medium risk, which means we need to implement immediate control measures to mitigate this risk.
5. Control Measures
To mitigate the risks identified during the assessment, the following control measures will be implemented:
- Working at Heights: Use of fall protection systems (harnesses, guardrails) and regular inspections of scaffolding.
- Heavy Machinery: Only trained and certified personnel will operate machinery. Clear visibility and warning signs will be posted.
- Electrical Safety: Lockout/tagout procedures will be enforced, and only qualified electricians will handle electrical work.
- Housekeeping: Regular site cleanup to minimize slip, trip, and fall hazards.
6. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
All personnel must wear the following PPE on-site:
- Hard hats
- High-visibility vests
- Safety boots
- Gloves
- Safety goggles
- Fall protection gear (as required)
7. Emergency Preparedness and Response
In case of an emergency, the following procedures will be followed:
- Evacuation Routes: Designated routes are clearly marked. Personnel will gather at the assembly point located at [Location].
- Emergency Contacts:
- Fire Department: [Insert Number]
- Ambulance: [Insert Number]
- HSE Officer: [Insert Number]
First Aid: A first aid station is set up on-site with trained personnel available during work hours.
8. Training and Competency
All employees, contractors, and subcontractors will receive HSE training prior to starting work. Training will include:
- Hazard awareness
- Safe operation of equipment
- Use of PPE
- Emergency response procedures
- Environmental protection measures
Refresher training will be conducted [monthly/quarterly], and records will be maintained.
9. Environmental Protection
To minimize environmental impacts, the following practices will be adopted:
- Waste Management: All waste, including hazardous materials, will be properly segregated and disposed of in compliance with local environmental laws.
- Dust Control: Water spraying and dust barriers will be used to minimize air pollution from construction activities.
- Noise Reduction: Work will be limited to designated hours, and noise barriers will be installed where necessary.
10. Monitoring and Reporting
Regular safety inspections will be carried out by the HSE Officer. A daily checklist will be used to ensure compliance with the HSE Plan. Any incidents, near misses, or environmental issues must be reported immediately to the HSE Officer, and corrective actions will be implemented.
Formula for Safety Performance Monitoring:
Safety performance can be measured using the Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) formula:

For example, if the project experienced 2 lost-time injuries over 500,000 hours worked:
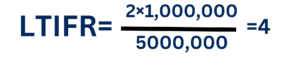
This indicates an LTIFR of 4, meaning 4 lost-time injuries per million hours worked.
11. Review and Revision
The HSE Plan will be reviewed every [time period] to ensure its effectiveness and updated if there are any changes in project scope, regulations, or safety procedures.
Approved by:
[Manager’s Name]
[Project Manager]
[Date]