HSE Trainings

BASIC OHS TRAINING

BASIC FIRE FIGHTING TRAINING

SCAFFOLDING INSPECTOR TRAINING

CONFINED SPACE ENTRY & RESCUE COURSE

BASIC FIRE FIGHTING TRAINING
BASIC OHS TRAINING

HABC FIRST AID AT WORK

BASIC FIRE FIGHTING TRAINING
IOSH-UK
Course Overview
IOSH is popular because of its short-term courses that it gives to all participants, as less time and money is invested in this course every industry prefer such courses need to be taken in their organisation.
Syllabus
- Module -1: Introducing managing safely.
- Module-2: Assessing risks.
- Module -3: Controlling risks.
- Module -4: Understanding responsibilities.
- Module -5: Understanding hazards.
- Module -6: Investigating incidents.
- Module -7: Measuring performance.
Who Should Attend
Course Methodology
The course includes relevant videos and written course material. Delivery of the course involves significant amounts of group discussion and small group work, with participants expected to feed back their assessments to the wider group for discussion.
Course Objectives
By the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Implement risk assessment methods to identify and rank health and safety risks within their business
- Develop controls to reduce or mitigate these risks to minimize business exposure
- Understand both personal and corporate responsibilities relating to health and safety
- Have an understanding of how to investigate incidents to reduce the likelihood of reoccurrence.
- Develop methods of measuring performance against health and safety targets.

Target Audience
- IOSH Managing Safely is designed for managers and supervisors in any sector, and any organization worldwide. The course provides the knowledge, skills and tools to tackle the safety and health issues that they’re responsible for.
- Importantly, Managing Safely makes a powerful case for safety and health being an integral part of day-to-day management and business.
Target Competencies
- Hazard identification
- Risk assessment and risk ranking
- Health and safety critical control selection and implementation
- Incident investigation tools
- Performance measurement
Note:
Successful participants are awarded an IOSH Managing Safely certificate.
NEBOSH IGC UK
International General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety
Duration
Assessment Type Assessment Time
Question Papers(IGC 1) 2 hours
Practical Assessment(IGC 2) 3 hours
About the course
NEBOSH International General Certificate is a globally recognized health and safety qualification intended for companies or individuals working to international standards with regards to Health, Safety & Environment. This course focuses on the International Labor Standards (ILO) codes of practice. Upon successful completion of the certificate, delegates can apply for a membership with Institution of Occupational Safety and Health (IOSH) and/or International Institute of Risk and Safety Management (IIRSM) as its qualification meets the academic requirements for Technician Membership (Tech IOSH) of IOSH and Associate membership (AIIRSM) of the IIRSM.
Unit IG2: Risk Assessment
- Physical and psychological health.
- Musculoskeletal health.
- Chemical and biological agents.
- General workplace issues.
- Work equipment.
- Fire.
- Electricity.
Assessment:
- Unit IG1 is assessed by a two-hour written examination.
- Unit IG2 is assessed by a three hour practical assessment carried out in your workplace (or another suitable workplace).
Exams are held in March, June, September and December each year.

ASNT NDT LEVEL II

Radiographic Testing:
Radiographic Testing (RT) is a nondestructive examination (NDE) technique that involves the use of either x-rays or gamma rays to view the internal structure of a component. In the petrochemical industry, RT is often used to inspect machinery, such as pressure vessels and valves, to detect for flaws. RT is also used to inspect weld repairs.
COURSES OVERVIEW
Dye Penetrant Testing:
Dye penetrant testing (DPT) or liquid penetrate testing (LPT) is a widely applied and low-cost inspection method used to check surface-breaking defects in all non-porous materials (metals, plastics, or ceramics). The penetrant may be applied to all non-ferrous materials and ferrous materials, although for ferrous components magnetic-particle inspection is often used instead for its subsurface detection capability. LPI is used to detect casting, forging and welding surface defects such as hairline cracks, surface porosity, leaks in new products, and fatigue cracks on in-service components.
Magnetic Particle Testing:
Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT), also referred to as Magnetic Particle Inspection, is a nondestructive examination (NDE) technique used to detect surface and slightly subsurface flaws in most ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, and some of their alloys. Because it does not necessitate the degree of surface preparation required by other nondestructive test methods, conducting MPT is relatively fast and easy. This has made it one of the more commonly utilized NDE techniques
Magnetic Particle Testing:
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. Ultrasonic testing is often performed on steel and other metals and alloys, though it can also be used on concrete, wood and composites, albeit with less resolution. It is used in many industries including steel and Aluminum construction, metallurgy, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive and other transportation sectors.
BASIC OHS TRAINING


Occupational Health & Safety Training
Course Objective:
This course introduces the candidate to many aspects of the Health & Safety at Work and is intended help raise safety standards and awareness. By the end of the course delegates will know how to manage safety effectively.
Course Content:
| Legal Requirement & Code of Practice |
| Introduction |
| Responsibilities of Employer and Employee |
| Hazard Identification Basic terms and definition Basic classification of Hazards Relevant principle methods of basic classifications |
| Fire Safety & Protection Awareness |
| Basic First Aid Awareness |
| Proper Handling, Storage and Transportation of Goods |
| Fall Prevention & Protection Awareness |
| Loading/Offloading of Equipment’s from Low-Bed |
| Safe Handling of Tools & Equipment |
| Basic Scaffold Erection & Dismantling |
| Housekeeping |
| Fire Safety&Electrical Safety |
| Substance (Drug & Alcohol) Abuse |
| Working at Height Safety |
| Proper Usage of PPE |
| Video & Practical Demo |
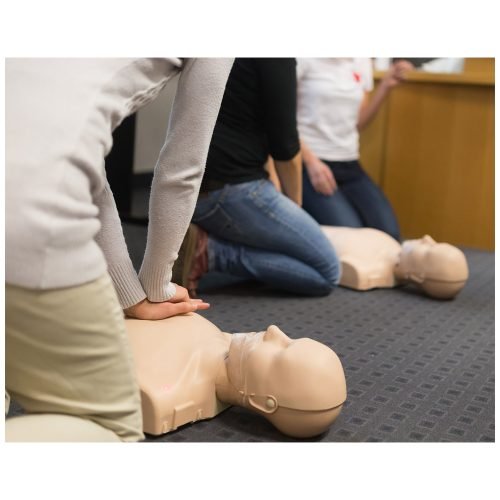
HABC FIRST AID AT WORK
Basic First Aid Training and Certification
Course Objective:
The provide participants knowledge in basic first aid that can be applied in the work area and relevant regulations and Accepted Code of Practice. At the end of the training, the participants will be able to learn and apply the below course contents.
Course Content:
| 1 | Legal Requiements & Code of Practice |
| 2 | Defining first aid& Duty Of care |
| 3 | CPR |
| 4 | Patient Assessment |
| 5 | Respiratory emergencies |
| 6 | Cardio pulmonary resuscitation |
| 7 | Recovery position |
| 8 | Bleeds and wounds |
| 9 | Muscular-skeletal injuries |
| 10 | Burns / chemical&Medical emergencies, diabetes, epilepsy, and poisoning |
| 11 | Video & Practical Demo |

BASIC FIRE FIGHTING TRAINING


Course Objective:
The purpose of this basic firefighting training is to give participants skills, knowledge and expertise that will enable them to identify the conditions capable of causing fire, know how to use a fire extinguisher, respond appropriately to fire emergencies and follow the fire evacuation plan, adequately implement fire emergency procedures.
Course Content:
| 1 | Legal Requirements & Code of Practice |
| 2 | Introduction to Fire &Classification of Fire |
| 3 | Fire Fighting System |
| 4 | Components of Fire Fighting System |
| 5 | Active and Passive Fire Protection |
| 6 | Fire Alarm Systems and Fire Hose Reel Cabinet |
| 7 | How to use a Fire Extinguisher |
| 8 | Fire emergency Preparedness |
| 9 | Video & Practical Demo |
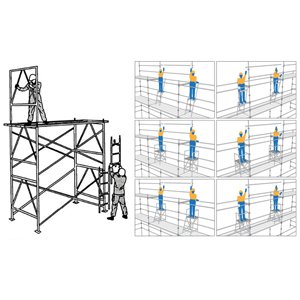
SCAFFOLDING INSPECTOR TRAINING
Course Objective:
The aims and objectives of Scaffolding Inspector training is to provide candidates with the working knowledge and skills in the methods of the basic safe erection and dismantling of basic scaffolds.
Course Content:
| 1. | Legal Requirements & Code of Practice |
| 2. | Definition of Scaffolds |
| 3. | Duty classes of scaffolding & Types |
| 4. | Planning scaffolding work |
| 5. | Hazard Associated with scaffolding |
| 6. | Ties & Braces |
| 7. | Inspection and maintenance |
| 8. | Types of scaffolding clamps & Inspection checklist |
| 9. | Video Presentation |


CONFINED SPACE ENTRY & RESCUE COURSE


Course Objective:
The Training provides Information on Safety Measures and Precautions to be taken before entering a Confined Space whenever job demands. Confined Space openings are limited primarily by Size or Location with opening is perhaps as small as 18 inches diameter and to access/egress is difficult. Information includes Potential Hazards and Risks associated with Confined Space Entry, Safety Precautions and on Personal Protective Equipments.
Course Content:
| 1 | Legal Requirments & Code of Practice |
| 2 | Potential Hazards and Risks &Risk Assessment |
| 3 | Safety Precautions and Mitigation |
| 4 | Atmosphere in a confined Space |
| 5 | Standby Supervision |
| 6 | Communication System |
| 7 | Isolation of the System |
| 8 | Disconnection of Electrical / Outside Connections |
| 9 | Usage of Personal Protective Equipments |
| 10 | Competency of the Worker |
| 11 | Presence of poisonous Gas/ Materials&Incident Reporting |
| 12 | Video & Practical Demo |
SAFE USE OF CRANE TRAINING
Course Objective:
To provide the basic skill requirements, practical application and associated job safety knowledge to personnel involved in Crane operations and signalingprocedures. At the end of the course, successful delegates should be able to operatecrane both safely and efficiently.
Course Content:
| 1 | Legal Requirements & Code of Practice |
| 2 | Safe Usage |
| 3 | Risk assessment |
| 4 | Types Cranes & Hoists |
| 5 | pre-use inspection |
| 6 | Handling the load Various types of load Types of rigging and slings Sling angle Trial Lifting |
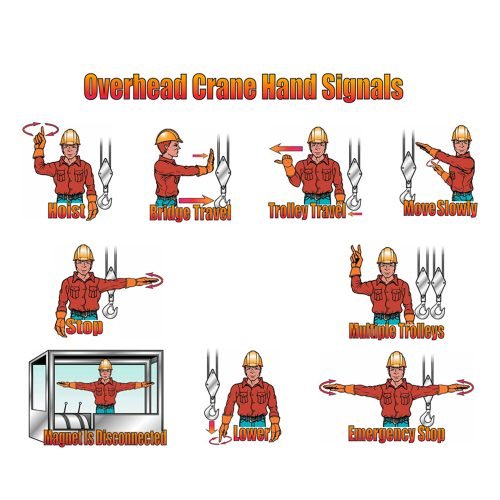
| 7 | Standard Hand signals |
| 8 | Safe Maintenance Practice |
| 9 | Selection & Usauge of Lifting accessories |
| 10 | Emergency preparedness&Usage of PPE’s |
| 11 | Hazards Involved in Operation |
| 12 | Safe handling technique&Operator competency |
| 13 | Video Presentation |