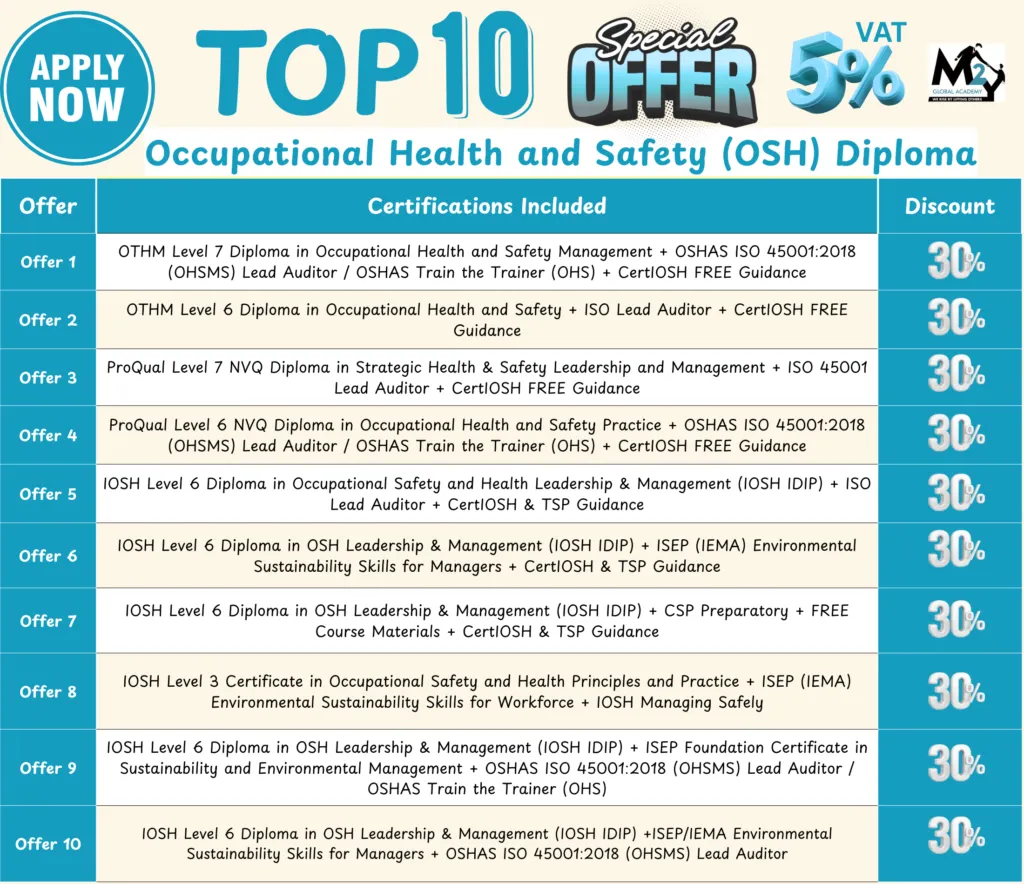
Safety Officer Course
Looking to build a career in workplace safety? A Safety Officer Course is your first step to becoming a certified safety professional.
From construction sites to oil refineries, safety officers play a vital role in protecting workers and ensuring regulatory compliance. If you’re someone who is passionate about preventing workplace accidents and promoting health and safety standards, then enrolling in a recognized Safety Officer Course could open up countless job opportunities across the globe.

What Is a Safety Officer Course?
A Safety Officer Course is a professional training program designed to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills to identify workplace hazards, implement safety measures, and ensure legal compliance. These courses cover both theoretical and practical aspects of occupational health and safety.
Core Topics Usually Covered:
Occupational Health and Safety Management
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
Fire Safety and Prevention
Emergency Planning and First Aid
Legal Safety Compliance
PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) Management
Popular Safety Officer Courses You Can Consider
M2Y Global Academy offers internationally recognized certifications that are ideal for aspiring safety officers:
1. NEBOSH IGC (International General Certificate)
One of the most preferred qualifications for safety professionals worldwide.
Duration: 1–2 months
Mode: Online or Classroom
Recognition: Globally accredited (UK-based)
2. IOSH Managing Safely
Perfect for beginners and managers wanting to implement workplace safety.
Duration: 3–5 days
Mode: Online/In-person
Certification: UK-certified
3. OSHA 30-Hour General Industry Training
Covers safety and health hazards commonly faced in general industry environments.
Duration: 30 hours
Mode: 100% Online
Certificate: Issued by US Department of Labor
4. Diploma in Industrial Safety
A comprehensive program designed for advanced safety responsibilities.
Duration: 6–12 months
Eligibility: After 12th / Graduation
Offered by: Recognized safety institutes
Who Should Take This Course?
Freshers aiming for a career in HSE (Health, Safety, and Environment)
Working professionals in industries like construction, oil & gas, manufacturing, logistics, etc.
Engineers and supervisors looking to upgrade their safety knowledge
Career switchers interested in roles with high job demand and global relevance
Career Opportunities After Completing Safety Officer Course
Once certified, candidates can pursue job roles such as:
| Job Role | Average Salary (Annual) | Industry Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Officer | ₹3 – ₹6 LPA (INR) / $40K–$70K | Construction, Oil & Gas, Logistics |
| HSE Engineer | ₹5 – ₹9 LPA / $50K–$80K | Manufacturing, Pharma, Refineries |
| Safety Supervisor | ₹2.5 – ₹5 LPA / $30K–$60K | Warehousing, Civil Infrastructure |
| Fire and Safety Inspector | ₹3 – ₹6 LPA / $40K–$65K | Airports, Government Sector |
| Risk Assessor | ₹6 – ₹10 LPA / $60K–$90K | Insurance, Corporate Sectors |
Why Choose M2Y Global Academy for Safety Officer Training?
✅ Global Certifications: NEBOSH, IOSH, OSHA & more
✅ Flexible Learning: Attend classes online or at our training centers
✅ Placement Assistance: We help connect you with top safety recruiters
✅ Expert Trainers: Learn from certified HSE professionals with real-time industry experience
✅ Affordable Fees: High-quality safety training at competitive rates
📞 Demo Class Available – Book Now!
🌐 Visit: https://m2yacademy.com/
What to Look for in a Safety Officer Course?
Here are a few important things to check before enrolling:
Accreditation: Is the course recognized by international bodies like NEBOSH, IOSH, or OSHA?
Trainer Expertise: Are trainers certified and experienced in real industry conditions?
Placement Support: Does the institute help with resume preparation or job assistance?
Reviews and Testimonials: Always check student feedback or success stories.
FAQs About Safety Officer Course
Yes, safety officers are in demand worldwide, especially in high-risk industries. The role offers job security, decent pay, and global mobility.
Most basic-level safety courses require 10th or 12th pass. Advanced diplomas or NEBOSH may require graduation or relevant experience.
Costs vary by course type and location. NEBOSH may cost ₹65,000 to ₹1,20,000 INR, while other diplomas may start at ₹25,000.
NEBOSH is highly preferred and often mandatory for international job roles, but not always required for local positions.
Final Thoughts
A career in occupational health and safety is not just professionally rewarding but also contributes to saving lives and improving work environments. Whether you’re a beginner or already working in the field, a Safety Officer Course will significantly enhance your credentials and open doors to global career opportunities.
👉 Ready to start your safety journey?
Enroll today at M2Y Global Academy and take your first step towards becoming a certified safety professional.